[ad_1]
Evaluation: The local weather papers most featured within the media in 2023
The 12 months 2023 noticed the coronation at Westminster Abbey of a brand new king, the mugshot of a former US president and the rebranding of a social media platform to a single letter.
However behind the largest tales of the 12 months, hundreds of research detailing new analysis additionally made the headlines. And local weather change and power have been among the many matters that acquired essentially the most consideration.
Annually, Altmetric tracks how usually analysis papers from tutorial journals are talked about in on-line information articles in addition to on blogs and social media platforms. It then offers every paper a rating in accordance with the eye it receives.
Utilizing Altmetric knowledge for 2023, Carbon Transient has compiled its annual listing of the 25 most talked-about climate- or energy-related papers that have been printed the earlier 12 months.
(The listing focuses on peer-reviewed analysis papers solely – commentaries or different papers that aren’t formally peer-reviewed will not be included.)
The infographic above reveals which papers made it into the highest 10, whereas the article contains evaluation of the complete listing of 25, together with the range of their authors and which journals characteristic most ceaselessly.
The listing covers analysis into the local weather projections of a significant oil firm, the human value of world warming and the catastrophic failure of breeding penguins – in addition to the curious case of the high-scoring paper that acquired nearly no information protection in any respect.
Antarctic ice cabinets
Essentially the most talked-about journal papers of 2023 are once more dominated by analysis referring to Covid-19, persevering with the sample seen lately.
For instance, the highest-scoring paper of any printed in 2023 is a evaluate into the effectiveness of measures to scale back the unfold of respiratory viruses, resembling Covid, swine flu and extreme acute respiratory syndrome (Sars).
The examine’s Altmetric rating of 25,730 places it nearly 10,000 factors forward of the second-placed paper, which can be about Covid.
However the top-scoring paper referring to local weather just isn’t far behind, touchdown fourth within the general listing with a rating of 13,886.
The examine, “Change in Antarctic ice shelf space from 2009 to 2019”, positive factors the best rating for any local weather paper in any of Carbon Transient’s annual opinions by a long way – the earlier highest was 7,803 in 2022.
(For Carbon Transient’s earlier Altmetric articles, see the hyperlinks for 2022, 2021, 2020, 2019, 2018, 2017, 2016 and 2015.)

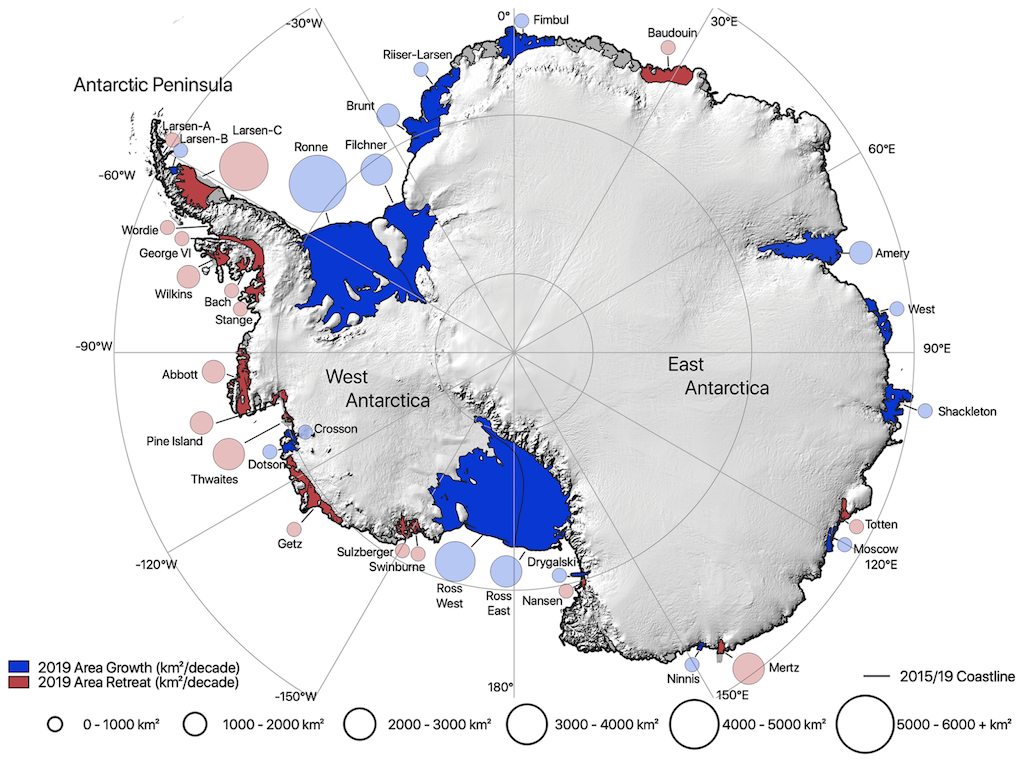
The examine, printed within the Cryosphere, makes use of satellite tv for pc observations to supply a dataset of modifications within the “calving entrance” – that’s, the place icebergs break off – and space of the ice cabinets that encompass Antarctica between 2009 and 2019. It reveals that, general, the realm of Antarctic ice cabinets has grown by round 5,300 sq. kilometres (km2) since 2009, with 18 ice cabinets retreating and 16 bigger cabinets rising in space.
Particularly, ice-shelf space has decreased on the Antarctic Peninsula (by 6,693km2) and in west Antarctica (by 5,563km2), and elevated in east Antarctica (by 3,532km2) and on the big Ross and Ronne-Filchner ice cabinets (by 14,028km2), the paper says.
The map from the examine beneath reveals the expansion (blue) and retreat (pink) of ice cabinets round Antarctica, the place the dimensions of the circles signifies the size of the change from 2009 to 2019.
Whereas the excessive scores of climate-related papers in earlier years have primarily been pushed by information protection, this paper seems in simply seven information tales.
As examine writer Prof Anna Hogg from the College of Leeds explains to Carbon Transient:
“Considerably unusually, we didn’t put out a press launch for the paper as we assumed the scientific group that wanted the dataset would make use of it naturally.”
As a substitute, the paper’s excessive Altmetric rating is principally a results of an enormous variety of mentions on Twitter – greater than 63,000 posts from round 48,000 accounts. (Altmetric contains weightings in its scoring system, so information articles (with a weighting of eight) are deemed to have extra influence than tweets (0.25).)
A more in-depth look means that the paper has been broadly quoted by the Twitter accounts of various distinguished local weather sceptics in an try to push again on issues round local weather change and the lack of Antarctic ice. These posts have then been broadly retweeted by different accounts.
To see the paper “getting used as proof to recommend that local weather change isn’t taking place” was a “actual shock”, says Hogg, as a result of the paper “doesn’t make any such assertion”.
Particularly, the positive factors the examine identifies in ice-shelf space in east Antarctica don’t detract from the dangers of retreating ice cabinets on different components of the continent, says Hogg:
“The lower in ice shelf space in west Antarctica is especially vital as this ice shelf space actively ‘buttresses’ the stream of ice from the ice sheet behind it, which by ice dynamic processes is likely one of the the explanation why west Antarctica is contributing considerably to present-day sea degree rise.”
Certainly, the seventh most-talked about paper in 2023 (see beneath) is a Nature Local weather Change examine warning that accelerated soften of west Antarctica’s ice cabinets is now locked in, even for essentially the most formidable emissions discount situations. The authors present this stark conclusion:
“These outcomes recommend that mitigation of greenhouse gases now has restricted energy to forestall ocean warming that would result in the collapse of the west Antarctic ice sheet.”
The deceptive manner the examine has been utilized by some climate-sceptic social media accounts has been “extremely difficult”, says Hogg, with the authors unable “to answer to each incorrect tweet” about their work. Nonetheless, they did discover “a good quantity” of responses from different accounts “saying that that they had learn the paper and it didn’t present proof in opposition to local weather change”.
This maybe reveals “open entry doing its job”, says Hogg, because the paper was printed in an open-access journal and so is freely accessible for anybody to learn. In one other high-scoring statistic, the complete paper has now been seen greater than 150,000 instances on the journal’s web site.
ExxonMobil
Touchdown in second place with an Altmetric rating of 8,686 is the evaluate paper, “Assessing ExxonMobil’s international warming projections”. Printed in Science, the examine analyses the worldwide warming projections documented and modelled by scientists on the oil main ExxonMobil between 1977 and 2003.
(There’s a higher-scoring paper, “The 2023 state of the local weather report: Coming into uncharted territory”, within the journal BioScience, however it’s a “particular report” and was not formally peer reviewed.)

The outcomes point out that “in non-public and tutorial circles for the reason that late Nineteen Seventies and early Eighties, ExxonMobil predicted international warming appropriately and elegantly”, the paper says, including:
“ExxonMobil’s common projected warming was 0.20C ±0.04C per decade, which is, inside uncertainty, the identical as that of impartial tutorial and authorities projections printed between 1970 and 2007.”
The findings reveal that ExxonMobil “knew as a lot as tutorial and authorities scientists knew” about international warming a long time in the past. However, the paper provides, “whereas these scientists labored to speak what they knew, ExxonMobil labored to disclaim it”.
The examine was lined by 823 information tales by 555 shops, together with BBC Information, the Related Press, CNN, Vice, CNBC and Inside Local weather Information. It was additionally included in 48 weblog posts and greater than 13,000 tweets. It’s the twelfth most talked-about paper on any subject in 2023.
Excessive warmth
In third place is the Nature Drugs paper, “Warmth-related mortality in Europe throughout the summer season of 2022”, with a rating of seven,821. The examine finds that greater than 60,000 deaths in the summertime of 2022 – Europe’s hottest season on report – have been linked to the warmth.

Throughout 35 nations, the best numbers of heat-related deaths occurred in Italy (18,010 deaths), Spain (11,324) and Germany (8,173), the examine says. It additionally finds that the “burden of heat-related mortality was increased amongst girls”, with 56% extra heat-related deaths in girls than males, relative to inhabitants.
The examine was picked up in 943 information tales from greater than 650 shops – the biggest variety of any paper within the high 25. It was picked up by shops throughout Europe, together with Sky Information and ITV Information within the UK, Agence France-Presse in France and Der Spiegel in Germany. Carbon Transient additionally lined the article intimately.
The widespread protection was more likely to be partially as a result of Europe was experiencing a heatwave dubbed “Cerberus” when the paper was printed in July.
Lead writer Dr Joan Ballester Claramunt from the Barcelona Institute for World Well being tells Carbon Transient that the paper additionally “acquired a lot consideration from the media as a result of society is more and more conscious of the well being dangers of environmental elements, and notably in a context of quickly warming temperatures”.
Remainder of the highest 10
In fourth place is, “Warning of a forthcoming collapse of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation”, which was printed in Nature Communications.
The examine makes use of statistical strategies to detect early warning indicators of a shutdown within the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation (AMOC), one of many main present programs on this planet’s oceans that performs an important position in regulating local weather.
Whereas assessments utilizing local weather mannequin simulations sometimes recommend that AMOC is “unlikely” to go a tipping level throughout the twenty first century, the examine says a collapse may happen “round mid-century below the present situation of future emissions”.
(One other paper that additionally makes use of observation-based early warning alerts to evaluate the soundness of AMOC featured in second place in Carbon Transient’s leaderboard for 2021.)
The paper’s Altmetric rating of 6,216 displays its widespread information protection, overlaying 672 tales from greater than 500 shops, together with the Washington Submit, Politico, El País, CNN and Der Spiegel.
The papers in fifth and ninth place each set out frameworks for assessing “protected” boundaries for the Earth to be a liveable place for people.
In fifth place with a rating of 5,411 is the Science Advances paper, “Earth past six of 9 planetary boundaries”. Offering the most recent evaluation of the boundaries that have been first established in 2009, the paper warns that “Earth is now properly outdoors of the protected working house for humanity”.
The ninth-placed paper, “Protected and simply Earth system boundaries”, shares various the identical authors and units out to quantify limits for “local weather, the biosphere, water and nutrient cycles and aerosols at international and subglobal scales”. When the paper was printed in Might, Carbon Transient reported on the blended response the paper acquired from different scientists, together with issues {that a} “self-selected group of scientists” have been defining the “protected house” for the planet.
In sixth place is the Science paper, “World glacier change within the twenty first century: Each improve in temperature issues”, which reveals a “sturdy linear relationship between international imply temperature improve and glacier mass loss”.
The examine tasks that glaciers outdoors of Antarctica and Greenland will lose between 26% and 41% of their collective mass by 2100, relative to 2015, below warming of 1.5C to 4C, respectively. Such a loss would trigger 49-83% of glaciers to vanish and see 90-154mm added to international sea ranges, the examine says.
In seventh place is the Nature Local weather Change paper, “Unavoidable future improve in West Antarctic ice-shelf melting over the twenty first century”, as talked about above. The findings, the authors say, current a “sobering outlook” for ice cabinets within the Amundsen Sea.
The paper made an look within the Science spherical of Carbon Transient’s annual quiz.
The eighth-placed paper is, Quantifying the human value of world warming, printed in Nature Sustainability. It quantifies this value when it comes to the variety of individuals left outdoors the “local weather area of interest” by which human civilisation has flourished for hundreds of years.
The examine reveals that local weather change has already put round 9% of individuals outdoors this area of interest, and that, by end-of-century, present insurance policies resulting in round 2.7C international warming may go away 22-39% of individuals outdoors the area of interest as properly.
Lastly, rounding out the highest 10 is, “Local weather extremes more likely to drive land mammal extinction throughout subsequent supercontinent meeting”, in Nature Geoscience.
The examine appears to be like on the prospects for people and different mammals on Earth primarily based on first-ever supercomputer local weather modelling of the distant future. The knock-on impacts of all Earth’s continents finally converging to kind the supercontinent “Pangea Ultima” would see enormous quantities of CO2 launched into the air by volcanic eruptions, it says.
The ensuing international temperatures of as much as 75C would, as a headline within the i newspaper put it, “sooner or later wipe out humanity – however not for one more 250m years”.
Elsewhere within the high 25
The remainder of the highest 25 contains a mixture of analysis, together with a paper on the impacts of El Niño on financial progress, a examine on the environmental impacts of several types of diets and evaluation of the quantity of world warming nonetheless “within the pipeline” by former Nasa scientist Dr James Hansen.
In 14th place is the Nature paper, “Assessing the dimensions and uncertainty of remaining carbon budgets”, which presents an up to date estimate of the remaining carbon finances for limiting warming to 1.5C and 2C.
In a 2022 Carbon Transient visitor put up, a number of the examine authors current an identical evaluation, concluding that the remaining carbon finances to restrict warming to 1.5C could possibly be simply 260bn tonnes of CO2 (GtCO2) – the equal of round six years of emissions. They add:
“Slicing international CO2 emissions to zero by 2050, consistent with limiting warming to 1.5C, would require them to fall by about 1.4GtCO2 yearly, akin to the drop in 2020 because of Covid-19 lockdowns all over the world, however this time pushed by a long-term, structural change of the financial system.
“This highlights that the size of the problem is immense, regardless of the exact determine of the quickly shrinking carbon finances.”
Antarctic sea ice made headlines all over the world each in 2022 and 2023, by setting two consecutive years of report low sea ice extent. In August 2023, researchers printed a sobering examine in Communications Earth and Surroundings below the title, “Report low 2022 Antarctic sea ice led to catastrophic breeding failure of emperor penguins”.
The examine finds that melting ice led to widespread “breeding failure” throughout Antarctic emperor penguin colonies and acquired widespread media consideration. It has been talked about in 537 information articles, producing headlines resembling, “1000’s of penguins die in Antarctic ice breakup”, from BBC Information and, “1000’s of penguin chicks killed by early sea ice breakup, examine says”, within the Washington Submit.
The Guardian, New Scientist and Day by day Telegraph have been among the many different publications that reported on the examine. This surge of consideration pushed the paper to fifteenth within the Carbon Transient rating, with an Altmetric rating of three,551.
In the meantime, the Lancet Countdown on well being and local weather change slipped down the rankings this 12 months. After three years within the Carbon Transient’s high 10, this 12 months’s report lands in twentieth place with an Altmetric rating of three,191.
The report is an epic annual publication, which opinions huge swathes of literature and has greater than 100 authors this 12 months. This 12 months’s report launched some key new indicators of the hyperlinks between local weather change and human well being. It was additionally the primary to incorporate projections on how the indications would possibly worsen in a hotter world.
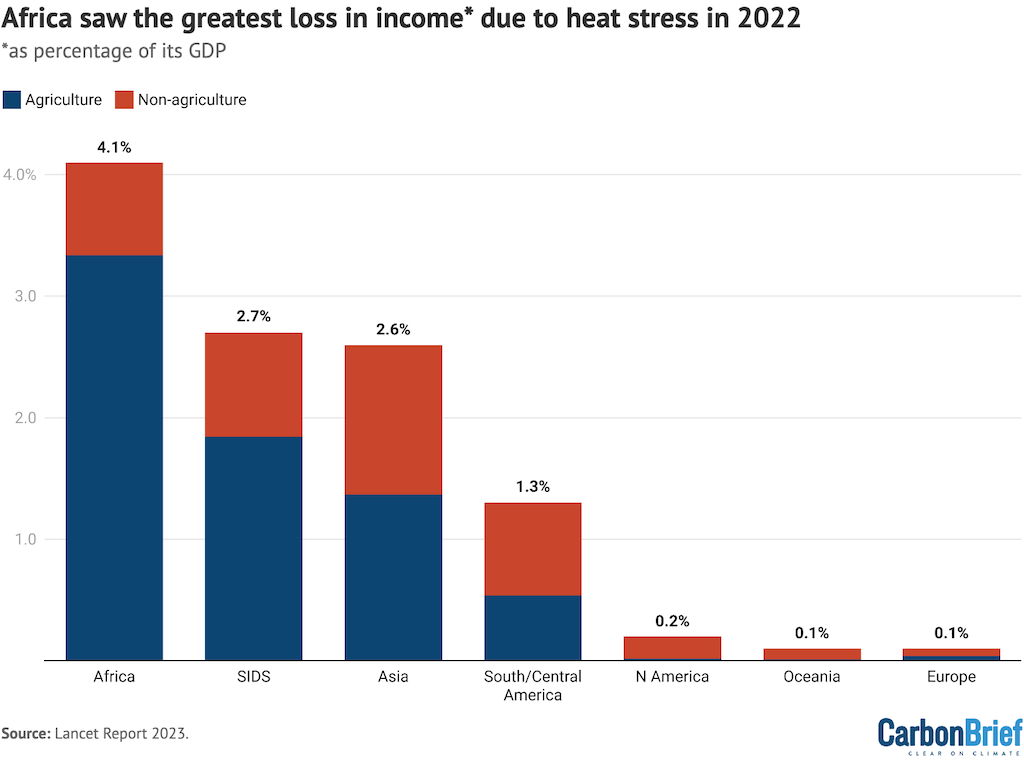
The report finds that lack of labour because of warmth publicity resulted in a $863bn lack of “potential revenue” in 2022. The agriculture sector was hit the toughest by the lack of labour, accounting for 82% of losses in least developed nations, the authors add.
Carbon Transient’s protection of the report highlights this lack of revenue because of warmth stress. The graph beneath reveals efficient revenue losses in 2022 because of warmth stress in agriculture (blue) and different sectors (pink), as a share of GDP, by continent.
One spot beneath the Lancet report is a Geophysical Analysis Letters examine which warns that local weather change is making air turbulence stronger and extra frequent. The findings, which have been picked up in additional than 500 information articles, have worrying implications for plane passengers.
Again in 2017, examine writer Dr Paul Williams wrote a Carbon Transient visitor put up warning that “essentially the most extreme [type of turbulence] – the type that may launch passengers out of their seats and trigger critical accidents – is ready to turn out to be twice and even 3 times as frequent by the latter half of the century”. And a latest Carbon Transient visitor put up on the quickest jet stream winds – referred to as “jet streaks” – additionally forecasts a rise in clear-air turbulence for plane passengers.
And in twenty fourth place is the Nature paper, “Glacial lake outburst floods threaten thousands and thousands globally”, with an Altmetric of two,991. The examine warns that 15 million individuals globally are uncovered to impacts of potential “glacial lake outburst floods” (GLOFs). (For extra on GLOFs, see Carbon Transient’s visitor put up from 2020, which explains how lakes fashioned by melting glaciers all over the world have elevated in measurement by 50% over the previous 30 years.)
High journals
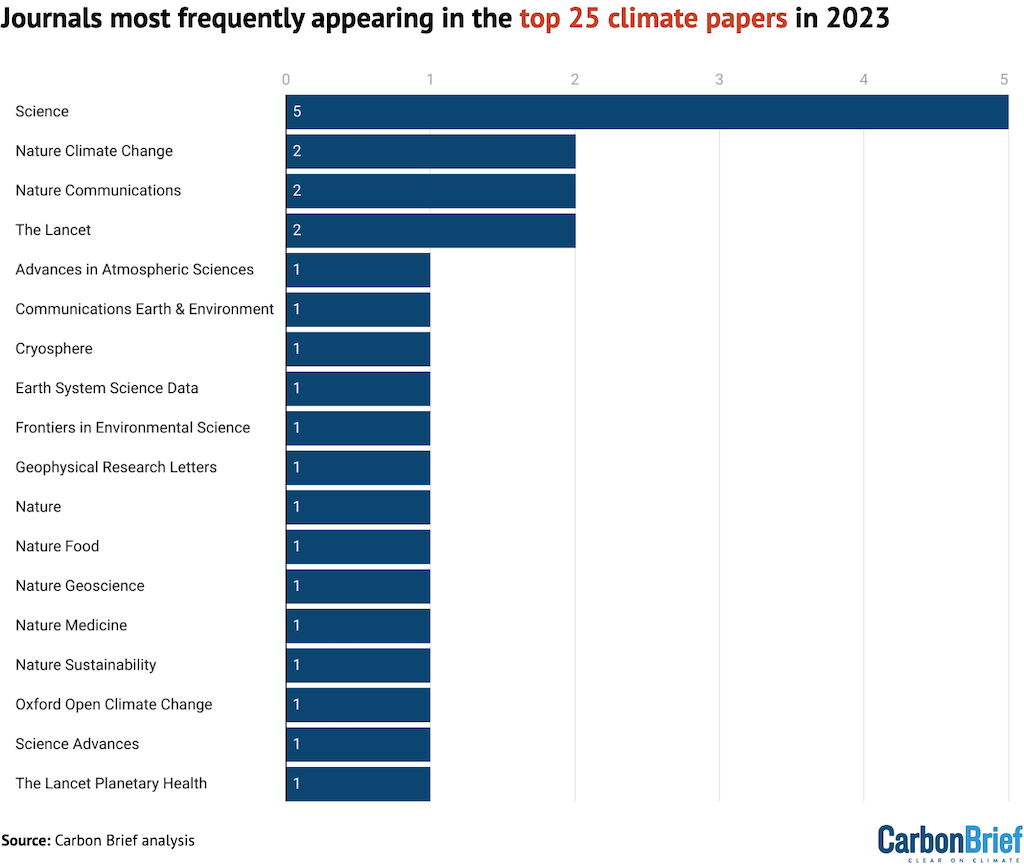
This 12 months there’s a clear winner for the journal with essentially the most papers that includes in Carbon Transient’s high 25: Science takes high spot with 5 papers.
Following Science are the three journals of Nature Local weather Change, Nature Communications and the Lancet, every with two papers within the high 25.
For the remainder of the highest 25, the remaining 14 journals seem as soon as every.
All the ultimate scores for 2023 could be discovered on this spreadsheet.
Variety of the highest 25
The highest 25 local weather papers of 2023 cowl an enormous vary of matters and scope. Nonetheless, regardless of the range within the local weather analysis the papers current, evaluation of their authors reveals a definite lack of variety.
In whole, the highest 25 local weather papers of 2023 have greater than 440 authors. Carbon Transient recorded the gender and nation of affiliation for every of those authors. (The methodology used was developed by Carbon Transient for evaluation offered in a particular 2021 collection on local weather justice.)
The evaluation reveals that the authors of the local weather papers most featured within the media in 2023 are predominantly males from the worldwide north.
The chart beneath reveals the institutional affiliations of all authors on this evaluation, damaged down by continent – Europe, North America, Oceania, Asia, South America and Africa.
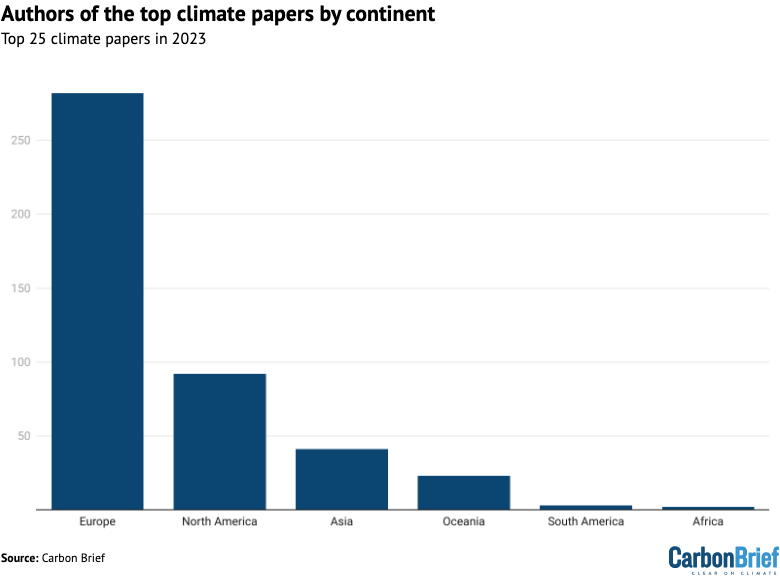
The evaluation reveals that 9 out of each 10 authors are affiliated with establishments from the worldwide north – outlined as North America, Europe and Oceania. In the meantime, solely six authors are from Africa and South America.
Additional knowledge evaluation reveals that there are additionally inequalities inside continents. The map beneath reveals the proportion of authors from every nation within the evaluation, the place darkish blue signifies a better share. Nations that aren’t represented by any authors within the evaluation are proven in white.
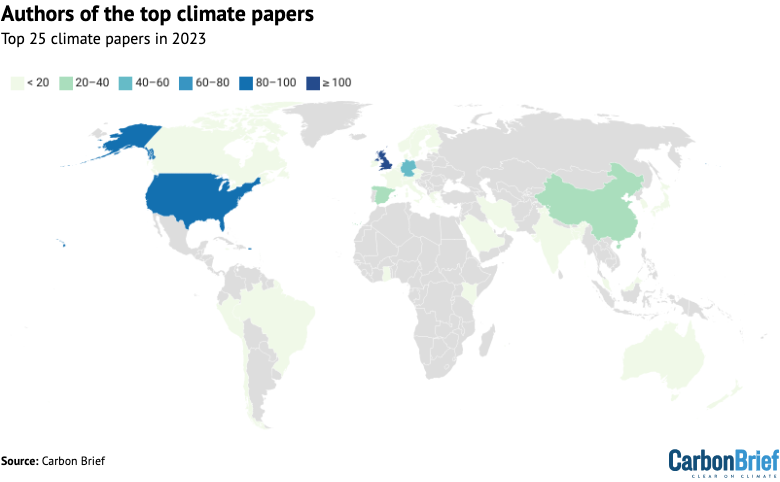
The highest-ranking nations on this map are the UK and the US, which collectively account for nearly half of all authors on this evaluation (25% and 18%, respectively).
Greater than half of all researchers from the worldwide south are from China – which accounts for round 6% of all researchers within the evaluation.
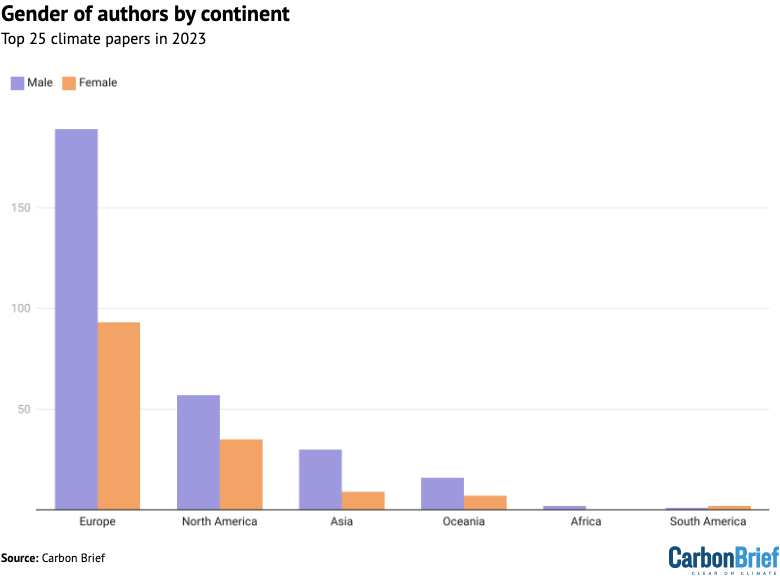
In the meantime, solely one-third of authors from the highest 25 local weather papers of 2022 are girls. Equally, solely seven of the 25 papers have a feminine lead writer.
The plot beneath reveals the variety of male (purple) and feminine (orange) authors on this evaluation from every continent.
The total spreadsheet displaying the outcomes of this knowledge evaluation could be discovered right here. For extra on the biases in local weather publishing, see Carbon Transient’s article on the shortage of variety in climate-science analysis.
This text was written by Robert McSweeney and Ayesha Tandon and edited by Leo Hickman. Knowledge evaluation was carried out by Robert McSweeney and Ayesha Tandon. The primary graphic was by Joe Goodman, and Kerry Cleaver and Ayesha Tandon contributed to the opposite visuals.
Sharelines from this story
[ad_2]
Source link



