[ad_1]
China accounted for 95% of the world’s new coal energy building exercise in 2023, in keeping with the most recent annual report from International Power Monitor (GEM).
Building started on 70 gigawatts (GW) of recent capability in China, up four-fold since 2019, says GEM’s annual report on the worldwide coal energy business.
This compares with lower than 4GW of recent coal energy building beginning in the remainder of the world – the bottom since 2014.
Exterior China, solely 32 international locations have new coal initiatives at pre-construction phases of growth and simply seven have crops underneath building.
Whereas world coal energy capability – each general and out of doors China – grew in 2023, GEM says that is prone to be a “blip” that can be offset by accelerating coal retirements within the subsequent few years within the US and Europe.
Different key findings of the report embrace that building of coal-fired energy crops globally – excluding China – declined for the second yr in a row. Nonetheless, coal energy plant retirements had been additionally on the lowest stage since 2011.
‘Pivotal juncture’ for China
In China, 47.4GW of coal energy capability got here on-line in 2023, GEM says. This enhance accounted for two-thirds of the worldwide rise in working coal energy capability, which climbed 2% to 2,130GW.
China’s 70.2GW of recent building getting underway in 2023 represents 19-times greater than the remainder of the world’s 3.7GW. Because the determine under highlights, the nation’s trajectory (crimson line) is diverging considerably from the remainder of the world (orange line).
The extent of recent building beginning in China is almost quadruple what it was in 2019, when the nation hit a nine-year annual low of completely new coal energy stations beginning.
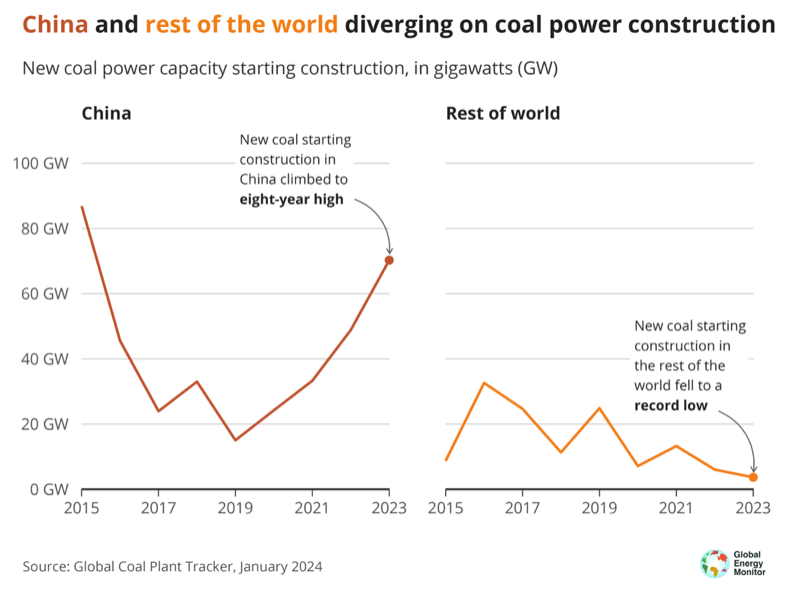
That is the fourth yr in a row that the quantity of recent coal building beginning has elevated in China. That is out of line with President Xi Jinping’s 2021 pledge to “strictly management” new coal energy capability, GEM states.
In early 2022, China’s Nationwide Power Administration’s 14th 5‐yr plan for a “trendy vitality system” said that 30GW of coal energy could be retired by 2025.
Nonetheless, when counting bigger coal items with capability of at the very least 30 megawatts, lower than 9GW of energy crops have been shut down within the final three years, and few others have plans to retire, GEM notes.
If China is to satisfy this 30GW retirement goal, it “must take fast motion”, GEM provides.
In an announcement, Qi Qin, China analyst on the Centre for Analysis on Power and Clear Air, mentioned:
“The current surge in coal energy growth in China starkly contrasts with the worldwide pattern, placing China’s 2025 local weather targets in danger. At this pivotal juncture, it’s essential for China to impose stricter controls on coal energy initiatives and expedite the transition in the direction of renewable vitality to realign with its local weather commitments.”
Collectively, China, India, Bangladesh, Zimbabwe, Indonesia, Kazakhstan, Laos, Turkey, Russia, Pakistan and Vietnam account for 95% of world pre-construction capability, in keeping with the GEM report.
The 5% remaining is distributed amongst 21 international locations, the tracker finds. Of those, 11 have one challenge and are on the point of attaining the “no new coal” milestone, it provides.
The tracker identifies 20.9GW of completely new coal energy proposals exterior of China in 2023. This was led by India, which noticed 11.4GW of recent coal capability proposed, greater than any yr since 2016. This was partially as a result of revival of a number of stalled initiatives within the nation, GEM explains.
Kazakhstan additionally noticed 4.6GW of recent proposals and Indonesia noticed 2.5GW. Some 4.1GW of beforehand shelved or cancelled capability is now thought-about “proposed” once more.
One other handful of nations – Russia, the Philippines, Botswana and Nigeria – additionally noticed revived proposals and building restarting in 2023.
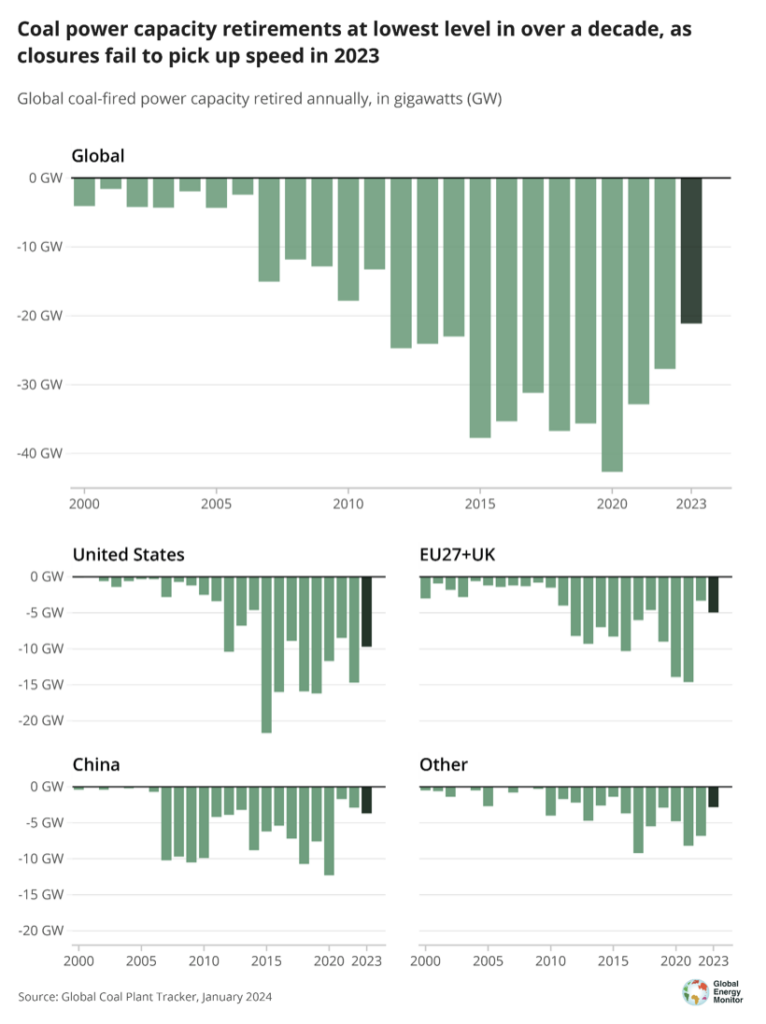
Retirements gradual
Globally, a complete of 69.5GW of coal energy got here on-line in 2023, whereas 21.1GW was retired, GEM finds. This led to the very best internet enhance in world working coal capability since 2016, with a 48.4GW leap.
New capability additionally got here on-line in Indonesia (5.9GW), India (5.5GW), Vietnam (2.6GW), Japan (2.5GW), Bangladesh (1.9GW), Pakistan (1.7GW), South Korea (1GW), Greece (0.7GW) and Zimbabwe (0.3GW).
In complete throughout 2023, the tracker discovered 22.1GW got here on-line and 17.4GW was retired exterior of China. This resulted in a 4.7GW internet enhance on the earth’s coal fleet working exterior China. Globally, coal energy capability reached 2,130GW in 2023, up from 2% a yr earlier.
The US contributed practically half of coal energy retirements, GEM says, with 9.7GW shuttering in 2023. Nonetheless, it is a drop in retirements from 14.7GW in 2022, and a peak of 21.7GW in 2015.
Elsewhere, the EU and UK represented practically 1 / 4 of retirements, with 3.1GW closing within the UK, 0.6GW in Italy and 0.5GW in Poland. There may be now only one working coal-fired energy plant within the UK, with the Ratcliffe-on-Soar set to shut in September 2024.
General, world coal energy plant retirements had been at their lowest stage since 2011, because the determine under reveals.
Exterior of China, the variety of coal-fired energy crops beginning building declined for the second consecutive yr, hitting its lowest stage since knowledge assortment started in 2015, GEM notes.
Lower than 4GW of recent initiatives started building exterior of China in 2023, far under the typical of 16GW between 2015 and 2022. Simply seven international locations began building, with one plant every in India, Laos, Nigeria, Pakistan and Russia, in addition to three crops in Indonesia.
Building has not began on any coal crops in Latin America since 2016, and none has began in Organisation for Financial Co-operation and Improvement (OECD), European or Center Jap international locations since 2019, GEM says.
Nigeria’s Ugboba energy station, positioned on the mine-mouth of the Idowu Falola Coal Mines within the Aniocha North native authorities space of Delta state, is the primary identified building of a coal energy plant in Africa since 2019, the report says.
The G7 – which accounts for 15% (310GW) of the world’s working coal capability, down from 32% (443GW) in 2015 – has no new coal capability underneath building. Nonetheless, there may be nonetheless one proposed coal energy plant in Japan and two within the US.
Each of the proposed websites within the US, the 0.4GW CONSOL Mission in Pennsylvania and the newly introduced 0.4GW Susitna energy station in Alaska, are anticipated to make use of carbon seize and storage applied sciences (CCS).
GEM says that these applied sciences are “successfully unsure and costly distractions from the pressing must section out coal”.
The G20 is residence to 92% of the world’s working coal capability (1,968GW) and 88% of pre-construction coal capability (336GW). Brazil, the present G20 chair, noticed its pipeline of pre-construction capability fall in 2023, however nonetheless has two potential initiatives remaining – the final pre-construction coal energy crops in Latin America.
No new coal nations
General, coal capability reached an all time excessive in 2023, GEM’s tracker says.
Working coal capability exterior China grew for the primary time since 2019, as much less coal capability retired than in every other single yr in additional than a decade, because the determine under reveals.
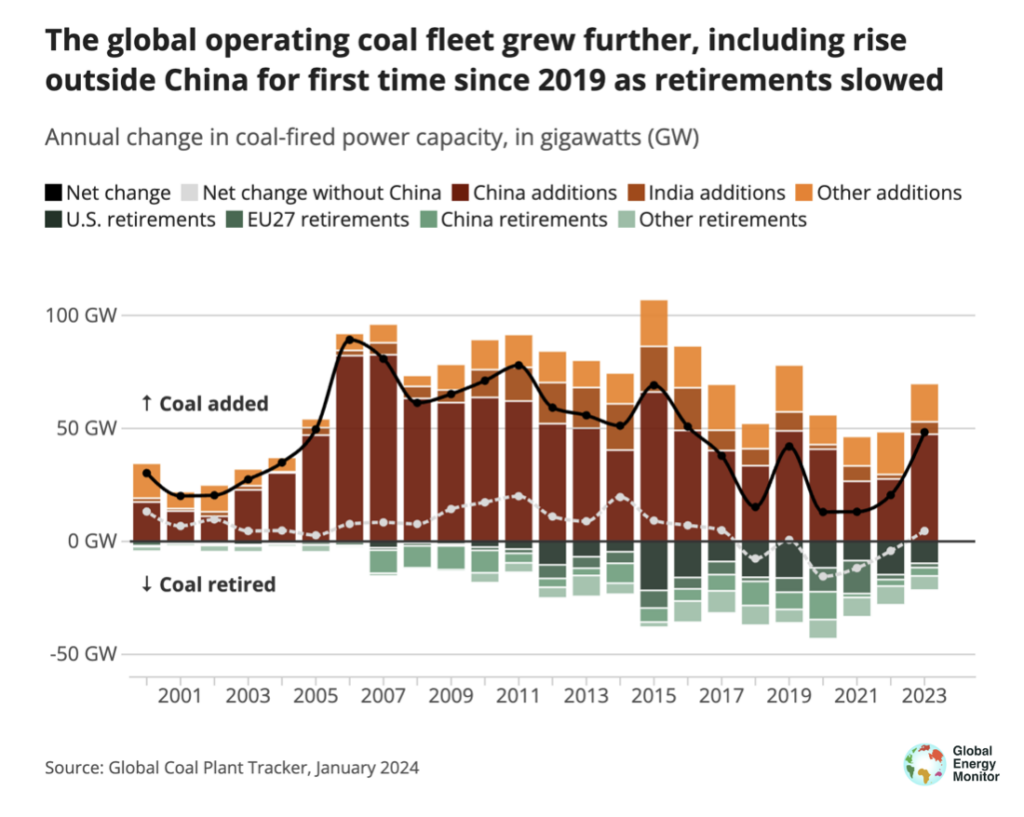
The world’s working coal energy capability is up 11% since 2015, when governments agreed to maintain the worldwide common temperature to properly under 2C above pre-industrial ranges and intention to restrict warming to 1.5C underneath the Paris Settlement.
Exterior of China, there are nonetheless 113GW of coal energy initiatives underneath building. Whereas that is solely barely up from the earlier yr’s stage of 110GW, it nonetheless highlights that the coal sector just isn’t according to the Worldwide Power Company’s (IEA) 1.5C state of affairs, GEM says.
Throughout all IEA eventualities that meet worldwide local weather objectives there’s a speedy decline in world coal emissions.
Globally, pre-construction capability rose 6% in 2023, “crystallising the significance of calls to cease proposing and breaking floor on new coal crops”, GEM’s report says.
Solely 15% (317GW) of at the moment working coal energy capability has a dedication to retire according to Paris Settlement objectives, it provides.
Phasing out unabated coal era by 2040 – according to the IEA’s 1.5C pathway – would require a median of 126GW of retirements yearly for the subsequent 17 years, GEM notes. That is the equal of two coal energy crops per week.
Even steeper cuts could be wanted to account for the 578GW of coal energy crops additionally underneath building and in pre-construction phases of growth, GEM says.
There have been 12 new international locations that dedicated to creating no new coal era in 2023, by becoming a member of the Powering Previous Coal Alliance. This brings the overall variety of international locations as much as 101 which have both formally declared they are going to haven’t any new coal or have deserted any coal plans they’ve had over the past decade, GEM notes.
Since 2015, there was a 68% discount in world pre-construction capability, GEM discovered. New building begins are actually at their lowest stage exterior of China, since knowledge assortment started.
GEM’s report means that coal energy initiatives that utilise CCS and people used to energy industrial actions could also be “a final frontier” for brand new coal proposals.
For instance, Zimbabwe’s 1.9GW of recent coal capability proposed in 2023 is made up of two initiatives, the Status energy station and the Gweru energy station, designed to energy smelters for extracting chromium from ore.
Zimbabwe is one among one six international locations, past China and India, to have elevated its complete deliberate capability over the previous yr, together with Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, Zimbabwe, the US and the Philippines.
At COP28, 130 international locations signalled their intent to section out unabated coal energy and cease investing in new unabated coal-fired energy crops inside this decade, by signing the International Renewables and Power Effectivity Pledge.
As well as, the ultimate world stocktake settlement at COP28 reiterated the pledge from COP26 to section down unabated coal energy, however nonetheless doesn’t outline what “unabated” means. Moreover, wording from earlier drafts on ending allowing of recent coal energy was omitted within the last textual content.
“Coal energy is on the fringe of a precipice, going through political and civil opposition and more and more uncompetitive economics,” GEM’s report states.
In an announcement, Flora Champenois, coal programme director for GEM mentioned:
“Coal’s fortunes this yr are an anomaly, as all indicators level to reversing course from this accelerated enlargement. However international locations which have coal crops to retire want to take action extra rapidly, and international locations which have plans for brand new coal crops should be sure these are by no means constructed. In any other case we are able to overlook about assembly our objectives within the Paris Settlement and reaping the advantages {that a} swift transition to wash vitality will carry.”
Sharelines from this story
[ad_2]
Source link



