[ad_1]

We’re in a important decade for motion on local weather change. The world is on monitor to expertise 3°C of warming and the “window of alternative to safe a habitable and sustainable future for all” is quickly closing. Nationwide governments are crucial systemic actors within the governance of local weather motion, primarily as a result of they’re the one actors with the power to undertake economy-wide decarbonization measures. Nonetheless, the overwhelming majority are failing to undertake and implement satisfactory mitigation insurance policies. States’ insufficient responses to the local weather disaster have pushed the rise of litigation instances in opposition to nationwide and sub-national governments. On this quick piece, we take inventory of developments in local weather litigation in opposition to governments, and determine three developments in future litigation – as communities globally preserve the stress on governments to halt additional harmful local weather change. Subsequent week’s judgments from the European Court docket of Human Rights in its first local weather instances might be one other important issue to form this area – so watch this house for extra evaluation to come back!
Stocktake of local weather litigation in opposition to governments
Over the previous decade, communities around the globe have turned to the courts to attempt to maintain their governments accountable for failing to behave on local weather change. ‘Framework’ or ‘systemic’ mitigation instances are people who problem a authorities’s total efforts to mitigate local weather change – encompassing each challenges to the ambition of emissions discount targets and/or their implementation. Over 80 authorities framework instances have been filed around the globe, utilizing all kinds of authorized and factual arguments. This consists of, for instance, the local weather case introduced by Korean younger folks earlier than the Constitutional Court docket of Korea, which is pictured above. Up to now, there have been quite a few profitable instances, together with selections issued by apex courts within the Netherlands, Germany, Eire, France, Colombia and Nepal.
Researchers have discovered that profitable framework instances in opposition to governments have had “a major affect on authorities decision-making, forcing governments to develop and implement extra bold coverage responses to local weather change.” Governments have been ordered to extend or replace their emissions discount efforts (e.g. Netherlands, Germany and just lately Belgium), to make clear their local weather plans (e.g. Eire and United Kingdom), and to implement their current targets (e.g. France). Reflecting these developments, the Worldwide Panel on Local weather Change (IPCC) has discovered that “local weather litigation can have an effect on the stringency and ambitiousness of local weather governance”.
Exterior of the courtroom, excessive profile litigation may shift the general public debate, driving the narrative that local weather motion is a authorized responsibility. For instance, quite a few framework instances in opposition to governments have acquired widespread public assist, and inspired public mobilisation on the urgency of local weather motion. Over two million folks signed a petition to assist the French local weather case, whereas almost 60,000 folks joined the Belgian local weather case as co-plaintiffs. Success in court docket in a single nation may create worldwide momentum for elevated mitigation ambition globally.
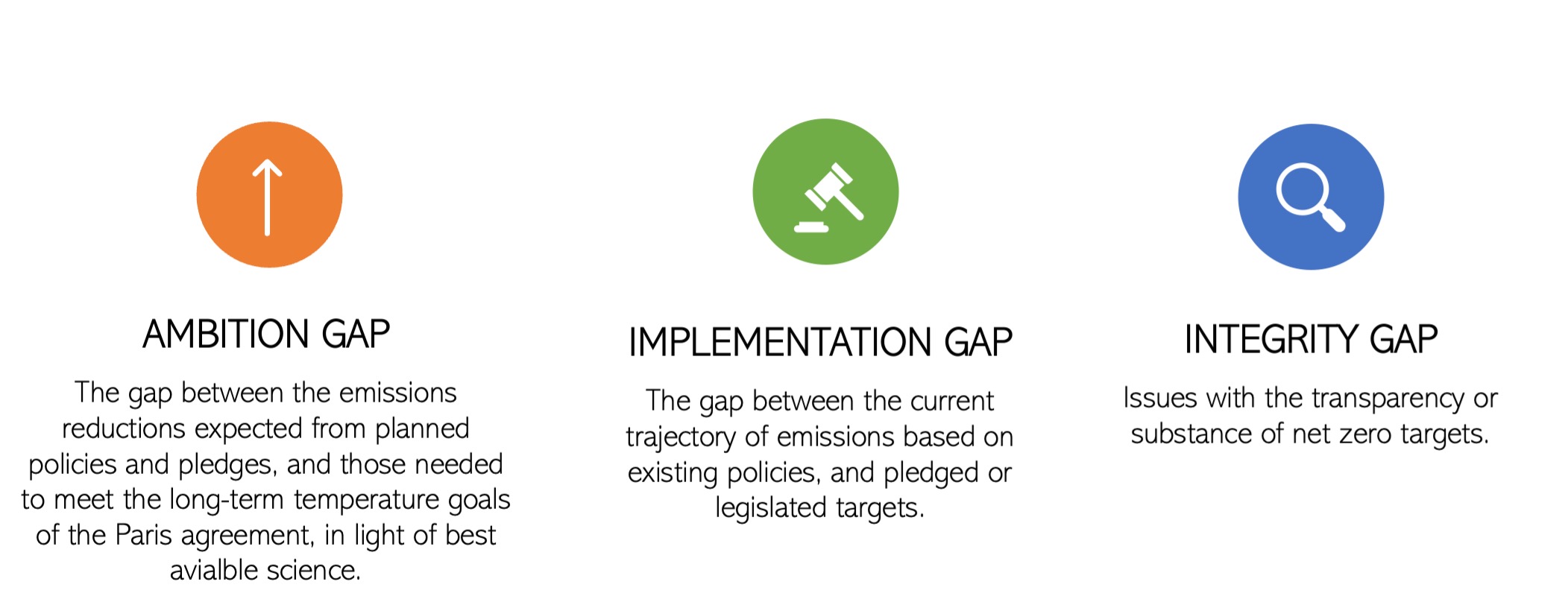
Up to now, framework local weather instances have largely centered on the ambition of governments’ total mitigation efforts, which we name the Ambition Hole. Right here, we outline the Ambition Hole because the distinction between the emissions reductions anticipated from a authorities’s deliberate insurance policies and pledges, and people required to satisfy the long-term temperature targets of the Paris Settlement, in gentle of greatest accessible science.
The rationale for this deal with the Ambition Hole is evident – regardless of the proliferation of net-zero pledges over latest years, governments’ efforts to cut back greenhouse fuel (GHG) emissions stay “woefully inadequate to satisfy the temperature aim of the Paris Settlement”. In line with the most recent UN report, revealed in November 2023, governments’ 2030 targets would result in a rise in international emissions of three% by 2030 – regardless of the necessity for international emissions to be slashed by a minimum of 43% by 2030 to maintain the 1.5°C temperature goal inside attain. The hole between international locations’ 2030 targets and 1.5°C pathways has remained important (round 19 GT of CO2 equal by 2030) and largely unchanged between 2021 and 2023. Specifically, rich, high-emitting international locations are failing to do their ‘fair proportion’ of emissions reductions to carry international warming to secure limits.
Out of the profitable instances to this point, judgments issued within the Netherlands, Germany and in Belgium have required, or brought about, the related authorities to extend the ambition of their emissions discount targets. Within the Netherlands and Belgium, the courts discovered that the related authorities(s) had an obligation of care beneath nationwide regulation and the European Conference of Human Rights to make sure that emissions discount targets have been ample for every nation to do ‘its half’ to carry international warming beneath harmful ranges, according to greatest accessible science. Each governments have been ordered to extend their emissions discount targets to exceed a minimal proportion recognized by the courts, based mostly on scientific proof. In Germany, the Constitutional Court docket discovered that the Authorities had a constitutional responsibility to make sure that its emissions discount targets wouldn’t result in future generations being subjected to drastic emissions reductions measures (i.e., because of the carbon price range getting used up in earlier years), which might considerably affect their basic freedoms. The European Court docket of Human Rights has been requested to adjudicate in two important ‘ambition’ instances – one in opposition to Switzerland, and one other in opposition to 33 Member States of the Council of Europe (amongst others). Communities in Europe and past eagerly await the Court docket’s judgments, which might be introduced on 9 April 2024.
Trying forward at local weather litigation in opposition to governments
The dimensions of the remaining Ambition Hole – as the most recent UN report underscores – signifies that litigation is more likely to preserve a deal with this space within the coming years. The forthcoming selections of the European Court docket of Human Rights within the two instances talked about above are more likely to have a major affect on the quantity, and framing, of future Ambition Hole instances – in Europe and past.
By way of rising developments, there are two key areas of litigation that we anticipate will turn into extra prevalent.
First, the Implementation Hole is changing into an more and more widespread – and essential – space of focus in framework instances. Lately, many governments have enshrined local weather targets in complete or framework local weather change laws – a constructive improvement in local weather governance. Sadly, in lots of international locations, there stays a major Implementation Hole between the present trajectory of emissions based mostly on current insurance policies, and the pledged or legislated targets. At current, governments are off monitor to implement even their (unambitious) current emissions discount targets. Closing the Implementation Hole might make a significant contribution to combating local weather change. In line with UN Atmosphere Program, with present (weak) implementation, insurance policies would result in round 3°C of warming. Full implementation of commitments beneath the Paris Settlement would decrease this estimate to 2.5°C. Looking to 2050, fulfilment of all net-zero pledges might restrict temperature rise to 2°C.
Up to now, there have been a number of profitable instances which have sought to drive governments to adjust to their current authorized obligations – to shut the Implementation Hole. Courts in Eire and the UK have ordered governments to extend the extent of element of their local weather plans, to make sure compliance with nationwide regulation. Courts in France have additionally ordered the Authorities to implement its current interim carbon budgets and 2030 goal, which have been set out in laws. Total, courts have been keen to interact with questions of compliance with nationwide local weather change laws. For instance, this consists of the enforcement of current nationwide targets, in addition to different authorized necessities regarding the well timed adoption of legally required insurance policies and transparency. We anticipate that this may encourage additional improvement and submitting of Implementation Hole instances.
Lastly, we anticipate points associated to the Integrity Hole in governments’ web zero targets to realize prominence in future instances. We outline the Integrity Hole broadly, to incorporate problems with transparency, as effectively substantive reliance on carbon dioxide removing (CDR) (e.g., the aim and nature of use, or the size of such reliance), in governments’ web zero targets. Most governments are failing to supply clear, bold and possible plans to ship on their guarantees – and are due to this fact missing a “credible path from 2030 in the direction of the achievement of nationwide net-zero targets”.
One key integrity concern focuses on the dearth of transparency and specificity about governments’ proposed reliance on CDR applied sciences to get to web zero emissions (and past). There’s a danger that governments are delaying near-term emissions reductions by counting on the longer term improvement of CDR. Whereas some governments (akin to Germany and Portugal) have adopted CDR targets separate to their emissions reductions targets to handle this, the overwhelming majority of nations haven’t taken this method.
Rich, high-emitting governments seem like counting on a scale of carbon removing and storage that’s far past the bodily limits of any at present accessible methods. Such massive scale reliance creates a excessive danger of future non-deployment, and important implications for human rights and ecological integrity.
Lately, main worldwide attorneys and local weather scientists revealed new analysis that warned that States which over-rely on future CDR to satisfy Paris Settlement targets might fall foul of worldwide regulation. The workforce referred to as for quicker cuts in GHG emissions and warned that governments might in any other case danger authorized challenges. Within the context of those dangers, local weather attorneys and authorized consultants have begun exploring authorized intervention avenues in opposition to over-reliance on CDR, in anticipation of the Integrity Hole changing into a brand new frontier in local weather litigation.
* This piece was initially ready for a convention on local weather litigation in Europe in November 2023 hosted by the Bonavero Institute of Human Rights, College of Oxford.
[ad_2]
Source link


